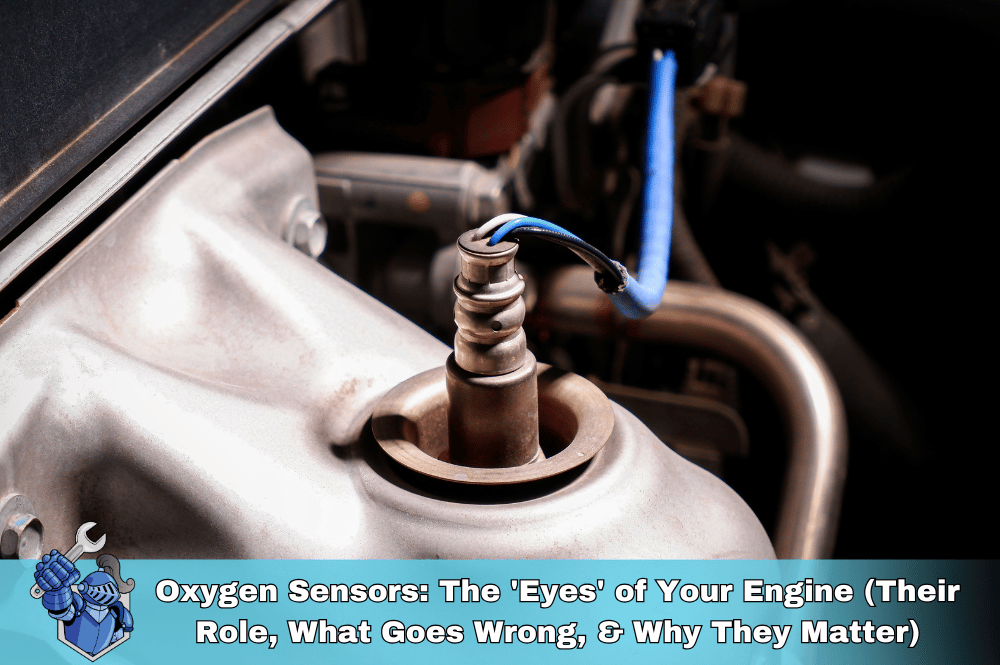
An oxygen sensor monitors the level of oxygen in your vehicle's exhaust gases. This data helps the engine's computer adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion, improving fuel efficiency and reducing harmful emissions.
If you’ve ever had your check engine light turn on mysteriously, chances are your oxygen sensor was involved. Often overlooked, this small component plays a critical role in keeping your vehicle running efficiently, cleanly, and safely. Think of it as the “eyes” of your engine control unit (ECU) — constantly monitoring your exhaust and making real-time adjustments to your air-fuel ratio. Without a properly functioning O2 sensor, your vehicle could be burning too much fuel, spewing emissions, or even damaging your catalytic converter.
In this ultimate guide, we’ll break down how oxygen sensors work, explore what oxygen sensors do, explain symptoms of a bad oxygen sensor, and walk through the replacement process, costs, and common issues. Whether you’re troubleshooting a P0420 code or just curious about O2 sensor function, this article is for you.
What Do Oxygen Sensors Do?
Oxygen sensors (or O2 sensors) measure the amount of oxygen in your vehicle’s exhaust gases and report this information back to the ECU. The computer then adjusts the fuel injection to optimize combustion.
- Too much oxygen = running lean (not enough fuel)
- Too little oxygen = running rich (too much fuel)
Proper combustion means better fuel efficiency, fewer emissions, and optimal engine performance. That’s why the O2 sensor is vital to your car emissions control system.
How Oxygen Sensors Work
Here’s the simplified science behind the sensor: inside the O2 sensor is a ceramic element coated with a conductive material. As hot exhaust gases pass over it, the sensor generates a voltage based on the oxygen content.
- A narrowband oxygen sensor provides a simple “rich” or “lean” signal.
- A wideband oxygen sensor offers precise oxygen level measurements, allowing finer control of fuel delivery.
Your car may have multiple sensors: typically one upstream oxygen sensor (before the catalytic converter) and one downstream oxygen sensor (after the converter). The upstream sensor monitors engine performance, while the downstream sensor checks if the catalytic converter is working effectively.
Types of Oxygen Sensors
There are several varieties of oxygen sensors, and knowing the difference can save time and money.
- Zirconia Sensors: The most common type in gasoline vehicles.
- Titania Sensors: Less common, use resistance rather than voltage.
- Wideband Sensors: Offer a full range of oxygen readings; common in modern vehicles.
- Narrowband Sensors: Older design; simpler, less accurate.
When replacing a sensor, always ensure you're matching the right type for your vehicle and its position (upstream vs. downstream oxygen sensor).

Symptoms of a Bad Oxygen Sensor
Knowing the symptoms of a bad oxygen sensor can help you catch problems early:
- Check engine light oxygen sensor code (often P0420 or P0133)
- Poor fuel efficiency
- Rough idling or stalling
- Black smoke from the exhaust
- Failed emissions test
- Rotten egg smell from the exhaust
- Engine misfires
Yes, a bad O2 sensor can cause misfires — especially if it’s leading to a rich fuel mixture.
Causes of Oxygen Sensor Failure
Like spark plugs, oxygen sensors wear out over time. Common causes include:
- Contaminants like oil, coolant, or silicone entering the exhaust stream
- High mileage – most sensors last 60,000 to 100,000 miles
- Carbon buildup
- Overheating or excessive exhaust temperatures
- Sensor heater failure (especially in the O2 sensor heater circuit)
When to Replace an Oxygen Sensor
So, how long do O2 sensors last? Most manufacturers recommend replacing them between 60,000 to 100,000 miles, but failure can occur sooner if your engine burns oil or runs rich.
If your vehicle logs trouble codes like P0133 (slow sensor response) or P0420 (catalyst efficiency), it may be time for a replacement.
You might also be wondering: Can you drive with a bad oxygen sensor? Technically, yes — but it’s not wise. Prolonged use can harm the catalytic converter, increase emissions, and waste fuel.
Oxygen Sensor Replacement Cost
The oxygen sensor replacement cost can range from $100 to $500+, depending on your vehicle and whether you replace it yourself or go to a mechanic.
- DIY cost: ~$50–$150 for the sensor, depending on type and brand
- Professional service: ~$200–$500, including labor
Labor costs go up if the sensor is hard to reach or rusted in place.

DIY: How to Test an Oxygen Sensor
Want to know how to test an oxygen sensor before replacing it? Here’s a basic rundown:
- Use an OBD-II scanner to read trouble codes.
- Inspect voltage: A healthy narrowband sensor should oscillate between 0.1 and 0.9 volts.
- Use a multimeter to check for power and ground in the sensor wiring.
- Look at O2 sensor voltage readings while the engine is running; consistent values may indicate failure.
Don’t forget: cleaning sensors with O2 sensor cleaner is usually ineffective. Most issues can’t be fixed with spray-on solutions.
The O2 Sensor’s Relationship to Other Parts
Oxygen sensors directly influence — and are influenced by — other vital systems:
- Catalytic converter: Downstream sensors verify if the converter is working.
- Fuel injectors: Controlled based on O2 sensor data.
- Air-fuel ratio sensor: A term often used for wideband sensors.
- Car emissions control system: Oxygen sensors are a pillar of emission regulation.
Faulty sensors = inaccurate fuel mixture = unburned fuel = clogged catalytic converter.
Where Is the Oxygen Sensor Located?
If you’re troubleshooting or planning a repair, here’s where to find your O2 sensor:
- Upstream sensor: Between the engine and catalytic converter (often in the exhaust manifold)
- Downstream sensor: After the catalytic converter (closer to the muffler)
Check your owner’s manual or a vehicle-specific oxygen sensor wiring diagram to identify exact placement.
Can a Bad O2 Sensor Affect Fuel Economy?
Absolutely. A bad oxygen sensor can trick your ECU into using the wrong air-fuel ratio, often causing a rich mixture. That means more fuel is burned than necessary, directly reducing fuel efficiency. You’ll spend more at the pump — sometimes losing 10-20% in mileage.
Why Oxygen Sensors Are So Important
So, why are oxygen sensors important? Because they:
- Help keep your engine running clean
- Improve fuel economy
- Protect your catalytic converter
- Reduce harmful emissions
- Maintain performance and drivability
Think of the O2 sensor as your car’s feedback loop. Without it, your engine is running blind.
Final Thoughts: Protecting Your Car and Wallet
Your vehicle’s oxygen sensors are crucial to its performance, emissions, and long-term health. They’re one of the most important — and most misunderstood — components under the hood. Ignoring a faulty O2 sensor can lead to higher costs down the road, from failing your next emissions test to replacing an expensive catalytic converter.
When you're looking to protect yourself from surprise repair bills, including sensor failures, consider getting a vehicle service contract from Noble Quote. Our plans often cover oxygen sensor replacement, along with hundreds of other vital components.
Want to learn more? Visit our Learning Center »
Everything You Need to Know About Oxygen Sensors: Real Answers to the Most Common Questions
What does an oxygen sensor do in a car?
What are the symptoms of a bad oxygen sensor?
Common signs include a check engine light, poor fuel economy, engine misfires, rough idling, and a strong exhaust odor. You may also fail an emissions test or notice black smoke from the tailpipe.
How do I know when to replace an oxygen sensor?
You should replace your oxygen sensor if you see diagnostic codes like P0133 or P0420, experience performance issues, or reach 60,000–100,000 miles (depending on your car’s manufacturer guidelines).
Can a bad O2 sensor affect fuel economy?
Yes. A failing oxygen sensor can cause your engine to run too rich or too lean, significantly reducing fuel efficiency—sometimes by up to 20%.
How much does it cost to replace an oxygen sensor?
Oxygen sensor replacement typically costs between $100 and $500. DIY replacement may be cheaper, while professional service may include labor fees.
What’s the difference between upstream and downstream oxygen sensors?
Upstream sensors are located before the catalytic converter and help manage fuel mixture. Downstream sensors, located after the converter, monitor emissions efficiency.
Can I drive with a bad oxygen sensor?
Yes, but it’s not recommended. Driving with a bad O2 sensor can increase emissions, damage your catalytic converter, and cost more in fuel and future repairs.
What causes oxygen sensors to fail?
Common causes include age, carbon buildup, engine oil contamination, coolant leaks, and high exhaust temperatures. Regular maintenance helps prevent premature failure.
How do you test an oxygen sensor at home?
Use an OBD-II scanner to read error codes, then a multimeter to check voltage readings. Normal narrowband sensors cycle between 0.1–0.9 volts while the engine is running.
Does an extended car warranty cover oxygen sensors?
Many vehicle service contracts, like those offered through Noble Quote, do cover oxygen sensor repairs. It’s best to review your plan or request a free quote to confirm.
Suggestions for you
Read MoreLet’s work together
Every week we showcase three charitable organizations that our donations are sent to. Our clients are able to choose which of these three will receive their gift when they add coverage to their vehicle...

 Kelley Blue Book Instant Cash Offer: Your Ultimate Guide to Getting Top Dollar for Your Car
Kelley Blue Book Instant Cash Offer: Your Ultimate Guide to Getting Top Dollar for Your Car The Ultimate Showdown: Car Broker vs. DIY Car Buying – Which Path Saves You More?
The Ultimate Showdown: Car Broker vs. DIY Car Buying – Which Path Saves You More? Spark Plugs: The Tiny Titans That Ignite Your Engine
Spark Plugs: The Tiny Titans That Ignite Your Engine Brake Pads: The Science of Stopping (How They're Made, What They Do, & Signs of Wear)
Brake Pads: The Science of Stopping (How They're Made, What They Do, & Signs of Wear) Farmers Auto Insurance: Your Ultimate 2025 Guide to Coverage, Rates & Savings
Farmers Auto Insurance: Your Ultimate 2025 Guide to Coverage, Rates & Savings Don't Miss Out: How to Buy Crypto Before the Next FOMO Wave (2025 Guide)
Don't Miss Out: How to Buy Crypto Before the Next FOMO Wave (2025 Guide) BYD Cars 2025: Your Ultimate Guide to the Full Lineup & Latest Innovations
BYD Cars 2025: Your Ultimate Guide to the Full Lineup & Latest Innovations The Importance of Wheel Alignment and Balancing: Smooth Driving and Tire Longevity
The Importance of Wheel Alignment and Balancing: Smooth Driving and Tire Longevity How to Maximize Your Car Trade-In Value: The Ultimate Guide
How to Maximize Your Car Trade-In Value: The Ultimate Guide Factors Affecting Your Car Insurance Rates: The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Costs
Factors Affecting Your Car Insurance Rates: The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Costs Reborn Rugged: Why the Ineos Grenadier is More Than Just an SUV
Reborn Rugged: Why the Ineos Grenadier is More Than Just an SUV AutoZone: Your DIY Partner or a Pro's Pit Stop? A Comprehensive Review
AutoZone: Your DIY Partner or a Pro's Pit Stop? A Comprehensive Review The 7 Hidden Costs of Skipping Your Extended Car Warranty
The 7 Hidden Costs of Skipping Your Extended Car Warranty Can You Afford the 6th Gen Camaro? A True Cost Breakdown
Can You Afford the 6th Gen Camaro? A True Cost Breakdown Online Used Car Shopping: What You NEED to Know Before You Buy
Online Used Car Shopping: What You NEED to Know Before You Buy Unlock Cheaper Rates: Your Ultimate Guide to State Farm Auto Insurance Discounts
Unlock Cheaper Rates: Your Ultimate Guide to State Farm Auto Insurance Discounts Your Car as an NFT? The Future of Automotive Ownership on Ethereum
Your Car as an NFT? The Future of Automotive Ownership on Ethereum Land Rover Evoque Review (2012–2024): True Cost of Ownership Revealed
Land Rover Evoque Review (2012–2024): True Cost of Ownership Revealed Porsche Macan: The REAL Cost of Ownership (2015–2024 Review)
Porsche Macan: The REAL Cost of Ownership (2015–2024 Review) Unlock Lower Rates: Your Guide to Travelers Auto Insurance Discounts
Unlock Lower Rates: Your Guide to Travelers Auto Insurance Discounts Noble Quote vs. Amber: Which Automotive Service Offers the Best Value?
Noble Quote vs. Amber: Which Automotive Service Offers the Best Value? Land Cruiser 2025: Unleashed & Uncosted!
Land Cruiser 2025: Unleashed & Uncosted! O'Reilly Auto Parts: Your Comprehensive Guide to Services, Products, and More
O'Reilly Auto Parts: Your Comprehensive Guide to Services, Products, and More The True Cost of Owning a G80 BMW M3: Beyond the Sticker Price
The True Cost of Owning a G80 BMW M3: Beyond the Sticker Price The Digital Garage for Your Dollars: Navigating the World of Trading Apps
The Digital Garage for Your Dollars: Navigating the World of Trading Apps Lost Keys? Noble Quote Has You Covered (and More!)
Lost Keys? Noble Quote Has You Covered (and More!) Nationwide Auto Insurance: 10 Essential Things to Know Before You Buy
Nationwide Auto Insurance: 10 Essential Things to Know Before You Buy The Ultimate Guide to Selling Your Car
The Ultimate Guide to Selling Your Car Capital One Auto Loans: Your Complete Guide to Financing Your Next Vehicle
Capital One Auto Loans: Your Complete Guide to Financing Your Next Vehicle Is the Cadillac ATS Worth It? A Review of Costs and Value
Is the Cadillac ATS Worth It? A Review of Costs and Value Comprehensive Review of the Nissan Altima: A Reliable Mid-Size Sedan
Comprehensive Review of the Nissan Altima: A Reliable Mid-Size Sedan Supporting Meals on Wheels NobleQuote's Commitment to Community Well-being
Supporting Meals on Wheels NobleQuote's Commitment to Community Well-being The Pros of an Extended Warranty: Why It’s Worth the Investment
The Pros of an Extended Warranty: Why It’s Worth the Investment Understanding Kia's Factory Coverage and the Value of an Extended Warranty
Understanding Kia's Factory Coverage and the Value of an Extended Warranty How Much Does a Car Warranty Cost? A Comprehensive Guide
How Much Does a Car Warranty Cost? A Comprehensive Guide The True Cost of Maintaining a Toyota: Is It Really as Affordable as You Think?
The True Cost of Maintaining a Toyota: Is It Really as Affordable as You Think? Toyota FJ Cruiser: A Comprehensive Review
Toyota FJ Cruiser: A Comprehensive Review The Importance of Choosing the Right Fuel for Your Vehicle: Why It Matters and How It Affects Your Auto Warranty
The Importance of Choosing the Right Fuel for Your Vehicle: Why It Matters and How It Affects Your Auto Warranty 4-Wheel Drive 4WD vs All-Wheel Drive AWD: What’s the Difference and Which Is Right for You?
4-Wheel Drive 4WD vs All-Wheel Drive AWD: What’s the Difference and Which Is Right for You? Manual Transmission vs. Automatic Transmission: Which is Right for You?
Manual Transmission vs. Automatic Transmission: Which is Right for You? Keep Your Engine Cool: The Must Have Guide to Car and Truck Water Pumps
Keep Your Engine Cool: The Must Have Guide to Car and Truck Water Pumps Understanding and Protecting Electric Vehicle Batteries: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding and Protecting Electric Vehicle Batteries: A Comprehensive Guide Why You Should Consider an Extended Warranty for Your Genesis
Why You Should Consider an Extended Warranty for Your Genesis Understanding Car Starters: Common Issues, Repair Costs, and How to Protect Your Vehicle
Understanding Car Starters: Common Issues, Repair Costs, and How to Protect Your Vehicle Honda Maintenance 101: Budgeting for Unexpected Repairs & Routine Service
Honda Maintenance 101: Budgeting for Unexpected Repairs & Routine Service Top Reasons Your Car Radiator Might Fail and How to Prevent Costly Repairs
Top Reasons Your Car Radiator Might Fail and How to Prevent Costly Repairs The Ultimate Guide to Motor Oil: Types, Benefits, and How to Change It
The Ultimate Guide to Motor Oil: Types, Benefits, and How to Change It Top 10 Dashboard Warning Lights Every Driver Should Know
Top 10 Dashboard Warning Lights Every Driver Should Know Famous Actors Who Have a Need for Speed: Hollywood's Race Car Drivers
Famous Actors Who Have a Need for Speed: Hollywood's Race Car Drivers Mastering the Art of Manual Transmission: A Comprehensive Guide to Driving Stick
Mastering the Art of Manual Transmission: A Comprehensive Guide to Driving Stick Comprehensive Review of the Honda Pilot: Your Ultimate Guide
Comprehensive Review of the Honda Pilot: Your Ultimate Guide Choosing the Right Brake Pads: A Complete Guide to Safety and Performance
Choosing the Right Brake Pads: A Complete Guide to Safety and Performance Top 5 Reasons Your Transmission May Be Failing: Expert Tips and Solutions
Top 5 Reasons Your Transmission May Be Failing: Expert Tips and Solutions Supporting a Worthy Cause: NobleQuote's Partnership with Alex's Lemonade Stand Foundation
Supporting a Worthy Cause: NobleQuote's Partnership with Alex's Lemonade Stand Foundation The Essential Guide to Car Maintenance: How to Keep Your Vehicle Running Smoothly
The Essential Guide to Car Maintenance: How to Keep Your Vehicle Running Smoothly Everything You Need to Know About Chevy Extended Warranties
Everything You Need to Know About Chevy Extended Warranties Are Lift Kits Covered Under Your Truck’s Extended Warranty? Key Info for Lifted Trucks
Are Lift Kits Covered Under Your Truck’s Extended Warranty? Key Info for Lifted Trucks How to Replace Your Car Key Battery Tips Costs and More
How to Replace Your Car Key Battery Tips Costs and More 8 Essential Tips to Avoid Overpaying at the Auto Repair Shop
8 Essential Tips to Avoid Overpaying at the Auto Repair Shop Subaru Outback Review: Everything You Need to Know About This Versatile SUV
Subaru Outback Review: Everything You Need to Know About This Versatile SUV Alternator Failing? Repair Costs, Symptoms, and Why You Need Coverage
Alternator Failing? Repair Costs, Symptoms, and Why You Need Coverage How to Choose the Best First Car for Your Teen in 2024: A Parent's Guide
How to Choose the Best First Car for Your Teen in 2024: A Parent's Guide Toyota Tacoma: The Definitive Buyer’s Guide & In-Depth Review
Toyota Tacoma: The Definitive Buyer’s Guide & In-Depth Review The Ultimate Guide to Vehicle Airbags: Everything You Need to Know to Stay Safe
The Ultimate Guide to Vehicle Airbags: Everything You Need to Know to Stay Safe Stranded on the Sidelines: Your Essential Guide to Roadside Breakdowns & Staying Safe
Stranded on the Sidelines: Your Essential Guide to Roadside Breakdowns & Staying Safe Dealer vs. Local Mechanic: Where Should You Take Your Car for Repairs?
Dealer vs. Local Mechanic: Where Should You Take Your Car for Repairs? The DIY Mechanic's Arsenal: Essential Tools for Basic Car Repairs
The DIY Mechanic's Arsenal: Essential Tools for Basic Car Repairs The Ultimate Guide to Automotive Wraps: Everything You Need to Know
The Ultimate Guide to Automotive Wraps: Everything You Need to Know Dodge Extended Warranty: Is It Worth the Cost? A Comprehensive Guide
Dodge Extended Warranty: Is It Worth the Cost? A Comprehensive Guide How Many Miles Can an Engine Really Last? The Definitive Guide
How Many Miles Can an Engine Really Last? The Definitive Guide Spotting and Stopping the Drip: Your Comprehensive Guide to Automotive Oil Leaks
Spotting and Stopping the Drip: Your Comprehensive Guide to Automotive Oil Leaks Electric vs. Gas Cars: The Ultimate Showdown for the Future of Driving
Electric vs. Gas Cars: The Ultimate Showdown for the Future of Driving 2024 BMW 3 Series Review: Is it Still the Ultimate Driving Machine?
2024 BMW 3 Series Review: Is it Still the Ultimate Driving Machine? Revving Up the Excitement: Unveiling the Magic of Disney Pixar's 'Cars'
Revving Up the Excitement: Unveiling the Magic of Disney Pixar's 'Cars' The Ultimate New Driver's Guide: Everything You Need to Know to Hit the Road with Confidence
The Ultimate New Driver's Guide: Everything You Need to Know to Hit the Road with Confidence Rules of the Road: Your Ultimate Guide to Safe Driving
Rules of the Road: Your Ultimate Guide to Safe Driving Exhaust Problems? Mufflers, Catalytic Converters, & Replacement Solutions
Exhaust Problems? Mufflers, Catalytic Converters, & Replacement Solutions Is the Ford Explorer Reliable? What Owners Need to Know
Is the Ford Explorer Reliable? What Owners Need to Know Ford Mustang: A Guide to Popular Models & Years (1964-Present)
Ford Mustang: A Guide to Popular Models & Years (1964-Present) What is an ASE Certified Mechanic? (And Why Should You Care)
What is an ASE Certified Mechanic? (And Why Should You Care) Looking for the Perfect Gift for a Car Enthusiast? Try These 10 Puzzles
Looking for the Perfect Gift for a Car Enthusiast? Try These 10 Puzzles Hope for the Warriors: Standing Strong for Our Veterans and Military Families
Hope for the Warriors: Standing Strong for Our Veterans and Military Families Shifting Gears: A Deep Dive into Extended Warranties for Automatic and Manual Transmissions
Shifting Gears: A Deep Dive into Extended Warranties for Automatic and Manual Transmissions Ford Bronco: A Legend Reborn – Explore its Wild History & Modern Muscle
Ford Bronco: A Legend Reborn – Explore its Wild History & Modern Muscle 7 Reasons Why the Chevrolet Chevelle Was More Than Just a Pretty Face
7 Reasons Why the Chevrolet Chevelle Was More Than Just a Pretty Face Should You Buy a Truck? The Ultimate Pros and Cons List
Should You Buy a Truck? The Ultimate Pros and Cons List Off-Roading vs. Overlanding: What’s the Difference?
Off-Roading vs. Overlanding: What’s the Difference? Is Your Car a Ticking Time Bomb? The Unexpected Costs of Car Ownership
Is Your Car a Ticking Time Bomb? The Unexpected Costs of Car Ownership Nissan Frontier: Conquer Any Terrain in Style and Comfort
Nissan Frontier: Conquer Any Terrain in Style and Comfort Car Trouble? Your Insurance Might NOT Cover This!
Car Trouble? Your Insurance Might NOT Cover This! Extended Warranty Secrets: Unlocking Surprising Perks You Didn’t Know Existed!
Extended Warranty Secrets: Unlocking Surprising Perks You Didn’t Know Existed! The Car Repair Lottery: Are You Feeling Lucky?
The Car Repair Lottery: Are You Feeling Lucky? 'Tis the Season to Be Jolly... and Protected: Why an Extended Warranty is the Gift That Keeps on Giving
'Tis the Season to Be Jolly... and Protected: Why an Extended Warranty is the Gift That Keeps on Giving Zombie Apocalypse Survival Tip #1: Get an Extended Warranty (Brains Not Included)
Zombie Apocalypse Survival Tip #1: Get an Extended Warranty (Brains Not Included) Ford F-150: This Ain't Your Grandpa's Pickup!
Ford F-150: This Ain't Your Grandpa's Pickup! Why Your Headlights Are Turning Yellow (And How to Prevent It)
Why Your Headlights Are Turning Yellow (And How to Prevent It) That Annoying Hemi Tick: Why It Happens & How to Stop It
That Annoying Hemi Tick: Why It Happens & How to Stop It Car Scratches Driving You Crazy? 10 Steps to Fix Them Yourself
Car Scratches Driving You Crazy? 10 Steps to Fix Them Yourself Ford Power Steering Repair: Problems & Solutions
Ford Power Steering Repair: Problems & Solutions 2015 Nissan Altima Warranty Expired? Get Extended Coverage Today!
2015 Nissan Altima Warranty Expired? Get Extended Coverage Today! Honda A/C Compressor Failure: Causes, Symptoms & Repair Costs
Honda A/C Compressor Failure: Causes, Symptoms & Repair Costs Save on Car Repairs: NobleQuote vs. Toco Extended Warranty Review
Save on Car Repairs: NobleQuote vs. Toco Extended Warranty Review 2016 Jeep Wrangler Extended Warranty: Coverage & Options
2016 Jeep Wrangler Extended Warranty: Coverage & Options Electric Vehicles 101: What You Need to Know Before Making the Switch
Electric Vehicles 101: What You Need to Know Before Making the Switch 2015 Ford Explorer: Avoid Costly Repairs with the Right Extended Warranty
2015 Ford Explorer: Avoid Costly Repairs with the Right Extended Warranty 2008 Toyota Camry: Common Repairs and Why Extended Coverage is a Smart Investment
2008 Toyota Camry: Common Repairs and Why Extended Coverage is a Smart Investment Maximize Your Tesla Warranty: Smart Strategies for Extended Coverage
Maximize Your Tesla Warranty: Smart Strategies for Extended Coverage Selling Your Car in 2025? Don’t Make These Mistakes!
Selling Your Car in 2025? Don’t Make These Mistakes! Tesla Cybertruck: Overpriced or Over-the-Top Awesome?
Tesla Cybertruck: Overpriced or Over-the-Top Awesome? Skip the Dealership: The Rise of Online Car Buying
Skip the Dealership: The Rise of Online Car Buying Car Safety Technology: How Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) Are Changing the Game (and Your Insurance Rates)
Car Safety Technology: How Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) Are Changing the Game (and Your Insurance Rates) Why Can’t I Include My Warranty in My Car Financing? Answers to Your Top Questions
Why Can’t I Include My Warranty in My Car Financing? Answers to Your Top Questions What to Do When the Dealership Makes Warranty Cancellation a Hassle
What to Do When the Dealership Makes Warranty Cancellation a Hassle Boost Your EV's Range: Tips and Tricks for Maximum Mileage
Boost Your EV's Range: Tips and Tricks for Maximum Mileage Is Cruise Control REALLY Saving You Fuel? The Truth Revealed
Is Cruise Control REALLY Saving You Fuel? The Truth Revealed Bumper to Bumper Extended Warranty: What Does it Really Mean?
Bumper to Bumper Extended Warranty: What Does it Really Mean? Why Is My Car Heater Blowing Cold Air?
Why Is My Car Heater Blowing Cold Air? Level Up Your EV Charging Knowledge: A Guide to Charger Types
Level Up Your EV Charging Knowledge: A Guide to Charger Types Selling Your Soul for an Extended Car Warranty (And Why They Keep Calling)
Selling Your Soul for an Extended Car Warranty (And Why They Keep Calling) Speaking Car: How to Clearly Communicate with Your Mechanic
Speaking Car: How to Clearly Communicate with Your Mechanic From Referrals to Reviews: Finding the Perfect Repair Shop for You
From Referrals to Reviews: Finding the Perfect Repair Shop for You Top 5 Most Expensive Car Repairs Your Manufacturer Warranty WON'T Cover
Top 5 Most Expensive Car Repairs Your Manufacturer Warranty WON'T Cover CarMax MaxCare vs. Noble Quote: Extended Warranty Showdown
CarMax MaxCare vs. Noble Quote: Extended Warranty Showdown Affordable Protection: Noble Quote vs. Autopom Warranty Pricing
Affordable Protection: Noble Quote vs. Autopom Warranty Pricing Avoid Costly Repairs: Noble Quote vs. Ox Car Care Warranties
Avoid Costly Repairs: Noble Quote vs. Ox Car Care Warranties Mercedes-Benz G-Class Review: On and Off-Road Performance, Features, and Price
Mercedes-Benz G-Class Review: On and Off-Road Performance, Features, and Price Don’t Buy a Honda Warranty Before Reading This! Noble Quote vs. HondaCare
Don’t Buy a Honda Warranty Before Reading This! Noble Quote vs. HondaCare Extended Warranty vs. Self-Insuring: Which Is Right for You?
Extended Warranty vs. Self-Insuring: Which Is Right for You? Best Extended Warranty for Your Ford: Noble Quote or Ford Protect?
Best Extended Warranty for Your Ford: Noble Quote or Ford Protect? Charging Your Peace of Mind: Using a Credit Card to Buy a Car Warranty
Charging Your Peace of Mind: Using a Credit Card to Buy a Car Warranty Noble Quote vs. Omega Auto Care: Which Auto Warranty Is Right for You?
Noble Quote vs. Omega Auto Care: Which Auto Warranty Is Right for You? Cadillac Escalade: Mastering the Maintenance
Cadillac Escalade: Mastering the Maintenance Knight Rider vs. Back to the Future: A Battle of the 80s Icons
Knight Rider vs. Back to the Future: A Battle of the 80s Icons 10 Things You Didn't Know About James Bond’s Aston Martin DB5
10 Things You Didn't Know About James Bond’s Aston Martin DB5 Cupid's Got Horsepower: Rev Up Your Valentine's Day!
Cupid's Got Horsepower: Rev Up Your Valentine's Day! Chevy Suburban Repair Guide: Common Problems
Chevy Suburban Repair Guide: Common Problems The Greatest NASCAR Rivalries of All Time: On-Track Battles and Off-Track Drama
The Greatest NASCAR Rivalries of All Time: On-Track Battles and Off-Track Drama 5 Car Problems That’ll Make You Wish You Had an Extended Warranty
5 Car Problems That’ll Make You Wish You Had an Extended Warranty Beyond F1: Exploring the World's Most Extreme Racing Series
Beyond F1: Exploring the World's Most Extreme Racing Series If NASCAR Had Car Warranties: The Pit Stop Chaos You’d See
If NASCAR Had Car Warranties: The Pit Stop Chaos You’d See The "New Car Smell" Doesn't Last Forever: Protecting Your Investment Long-Term
The "New Car Smell" Doesn't Last Forever: Protecting Your Investment Long-Term Forza: The Perfect Blend of Simulation and Arcade Fun
Forza: The Perfect Blend of Simulation and Arcade Fun Warranty Myths Busted: Don't Fall for These Common Misconceptions
Warranty Myths Busted: Don't Fall for These Common Misconceptions The Future of Racing: Electric Cars, Autonomous Vehicles, and Beyond
The Future of Racing: Electric Cars, Autonomous Vehicles, and Beyond We've Moved! Noble Quote's New Home at the Lake of the Ozarks
We've Moved! Noble Quote's New Home at the Lake of the Ozarks Porsche Cayenne Engine Problems: What to Watch For
Porsche Cayenne Engine Problems: What to Watch For The Most Common Car Breakdowns of 2025 (And How to Avoid Them)
The Most Common Car Breakdowns of 2025 (And How to Avoid Them) Supercar Dreams on a Budget: The Most Affordable Exotics for First-Time Buyers
Supercar Dreams on a Budget: The Most Affordable Exotics for First-Time Buyers Chevy Malibu Ownership: Staying Ahead of the Repair Curve
Chevy Malibu Ownership: Staying Ahead of the Repair Curve Mazda Extended Warranty: Your Comprehensive Guide
Mazda Extended Warranty: Your Comprehensive Guide Protect Your Car & the Planet: Introducing NobleQuote's Green Choice Program
Protect Your Car & the Planet: Introducing NobleQuote's Green Choice Program Subaru Extended Warranty: Your Ultimate Guide
Subaru Extended Warranty: Your Ultimate Guide Ford Raptor Extended Warranty Guide: Conquer the Road with Confidence
Ford Raptor Extended Warranty Guide: Conquer the Road with Confidence Dodge TRX: King of the Off-Road
Dodge TRX: King of the Off-Road Kansas City Chiefs Players: You Won’t Believe What They’re Driving!
Kansas City Chiefs Players: You Won’t Believe What They’re Driving! Porsche GT3: Beyond the Numbers – The Soul-Stirring GT3 Experience
Porsche GT3: Beyond the Numbers – The Soul-Stirring GT3 Experience The Truck Owner’s Peace of Mind: Why Noble Quote Leads the Pack in Truck Repair Protection
The Truck Owner’s Peace of Mind: Why Noble Quote Leads the Pack in Truck Repair Protection Rivian R1S Review: Is This the Ultimate Electric Adventure SUV? (2025)
Rivian R1S Review: Is This the Ultimate Electric Adventure SUV? (2025) Protecting Your Ride Like Jalen Protects the Pocket: Cars, Eagles, and Smart Investments
Protecting Your Ride Like Jalen Protects the Pocket: Cars, Eagles, and Smart Investments Beyond Coverage: How Extended Warranties Can Expedite Your Car Repairs Amid Supply Chain Challenges
Beyond Coverage: How Extended Warranties Can Expedite Your Car Repairs Amid Supply Chain Challenges Keeping vs. Selling: Weighing Your Car Options & the Value of an Extended Car Warranty
Keeping vs. Selling: Weighing Your Car Options & the Value of an Extended Car Warranty DIY Oil Change: Do It Better Than the Pros (and Save Money!)
DIY Oil Change: Do It Better Than the Pros (and Save Money!) Nissan Pathfinder Common Problems: A Complete Repair Guide
Nissan Pathfinder Common Problems: A Complete Repair Guide Noble Quote: Driving with Confidence, Protected from Unexpected Repairs
Noble Quote: Driving with Confidence, Protected from Unexpected Repairs Ferrari vs. Lamborghini: A History of Innovation and Rivalry
Ferrari vs. Lamborghini: A History of Innovation and Rivalry What Happens to My Vehicle Service Contract If I Sell My Car?
What Happens to My Vehicle Service Contract If I Sell My Car? What to Do If Your Vehicle Service Contract Claim Is Denied
What to Do If Your Vehicle Service Contract Claim Is Denied Vehicle Service Contracts for SUVs and Trucks: Protecting Your Investment
Vehicle Service Contracts for SUVs and Trucks: Protecting Your Investment Maximize Your Savings: Understanding Your Vehicle Service Contract Deductible Options
Maximize Your Savings: Understanding Your Vehicle Service Contract Deductible Options Navigating the Online Vehicle Marketplace: Your Comprehensive Guide to Finding the Perfect Car or Truck
Navigating the Online Vehicle Marketplace: Your Comprehensive Guide to Finding the Perfect Car or Truck Don’t Get Stuck With Repair Bills: Ford Edge Warranty Coverage Explained
Don’t Get Stuck With Repair Bills: Ford Edge Warranty Coverage Explained Stop Paying for Potholes: The Smart Way to Protect Your Wheels and Tires
Stop Paying for Potholes: The Smart Way to Protect Your Wheels and Tires Extended Car Warranty with Active Factory Coverage: Smart Move or Waste of Money?
Extended Car Warranty with Active Factory Coverage: Smart Move or Waste of Money? Recession-Proof Your Ride: Why an Extended Car Warranty Makes Sense Now
Recession-Proof Your Ride: Why an Extended Car Warranty Makes Sense Now RV Road Trip Ready: Secure Your Adventures with Extended Warranty Coverage
RV Road Trip Ready: Secure Your Adventures with Extended Warranty Coverage What is a Home Warranty and Do You Need One?
What is a Home Warranty and Do You Need One? NobleQuote: Best Auto Protection, Not Just the Oldest
NobleQuote: Best Auto Protection, Not Just the Oldest Kia Telluride Review: Unpacking the Features and the Real Cost to Own
Kia Telluride Review: Unpacking the Features and the Real Cost to Own Bitcoin vs. Cash: A Head-to-Head Comparison of Features
Bitcoin vs. Cash: A Head-to-Head Comparison of Features Beyond the Hype: A Realistic Look at Hyundai Ioniq 5 Ownership Costs and Performance
Beyond the Hype: A Realistic Look at Hyundai Ioniq 5 Ownership Costs and Performance Unlock Better Opportunities: Your Guide to Understanding and Improving Your Credit Score
Unlock Better Opportunities: Your Guide to Understanding and Improving Your Credit Score Safe Kids: Your Comprehensive Guide to Child Car Seat Installation Tips and Guidelines
Safe Kids: Your Comprehensive Guide to Child Car Seat Installation Tips and Guidelines Chevy Colorado: Unpacking the Features and the Real Cost of Ownership
Chevy Colorado: Unpacking the Features and the Real Cost of Ownership Don’t Let Tariffs Hike Your Bills: The Smart Way an Extended Warranty Saves You on Car Repairs
Don’t Let Tariffs Hike Your Bills: The Smart Way an Extended Warranty Saves You on Car Repairs Drive Smart, Save Smarter: Your Guide to Budgeting for Car Care
Drive Smart, Save Smarter: Your Guide to Budgeting for Car Care Tech Troubles Ahead? The Rising Costs of Modern Vehicle Repairs
Tech Troubles Ahead? The Rising Costs of Modern Vehicle Repairs The Downtime Trap: How Car Repairs Can Cost You More Than Just the Bill
The Downtime Trap: How Car Repairs Can Cost You More Than Just the Bill DIY Danger? The Financial Risks of Handling Car Repairs Yourself
DIY Danger? The Financial Risks of Handling Car Repairs Yourself Smart Buyer’s Guide: Ford F-250 Review and Long-Term Ownership Costs (2022–2024)
Smart Buyer’s Guide: Ford F-250 Review and Long-Term Ownership Costs (2022–2024) Depreciation Demystified: Planning for Your Car’s Future Value
Depreciation Demystified: Planning for Your Car’s Future Value New vs. Used: A Financial Showdown for Your Next Vehicle
New vs. Used: A Financial Showdown for Your Next Vehicle Beyond Self-Driving: OpenAI and the Next Generation of Automotive Intelligence
Beyond Self-Driving: OpenAI and the Next Generation of Automotive Intelligence Blockchain Basics: The Technology Behind Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain Basics: The Technology Behind Cryptocurrencies Living with a Legend: The Hidden Costs of Dodge Challenger Hellcat Ownership
Living with a Legend: The Hidden Costs of Dodge Challenger Hellcat Ownership The Crypto Long Game: Proven Strategies for Building Generational Wealth
The Crypto Long Game: Proven Strategies for Building Generational Wealth Family First, Finances Second? The Real Cost of Owning a Toyota Highlander
Family First, Finances Second? The Real Cost of Owning a Toyota Highlander Understanding Car Leasing: A Complete Guide for First-Timers
Understanding Car Leasing: A Complete Guide for First-Timers Drive Away Richer? Credit Card Secrets for Smart Car Buying
Drive Away Richer? Credit Card Secrets for Smart Car Buying The EV Territory Wars: US Automakers Fight for Survival
The EV Territory Wars: US Automakers Fight for Survival From Solid Axle to Supercar: The Ultimate Guide to Every Corvette Generation (C1–C8)
From Solid Axle to Supercar: The Ultimate Guide to Every Corvette Generation (C1–C8) Hello, Robot Neighbor: The Dawn of Everyday AI and Its Impact
Hello, Robot Neighbor: The Dawn of Everyday AI and Its Impact Beyond the Movie: The Gritty Truth of Ford vs. Ferrari
Beyond the Movie: The Gritty Truth of Ford vs. Ferrari Slash Your Car Insurance Bills: Expert Tips You Need Now
Slash Your Car Insurance Bills: Expert Tips You Need Now Chevy Equinox: The Honest Truth – Pros, Cons, and Everything In Between (Including Cost of Ownership)
Chevy Equinox: The Honest Truth – Pros, Cons, and Everything In Between (Including Cost of Ownership) Decoding Auto Insurance: Your Easy-to-Understand Guide
Decoding Auto Insurance: Your Easy-to-Understand Guide Pessada Holdings: BBB A+ Rated Excellence
Pessada Holdings: BBB A+ Rated Excellence Save More, Stress Less: Family Budgeting Tips That Work
Save More, Stress Less: Family Budgeting Tips That Work Slate’s Electric Entry: A Deep Dive into the New Automotive Truck
Slate’s Electric Entry: A Deep Dive into the New Automotive Truck Affordability Crisis: How Rising Costs are Putting the Brakes on Car Sales
Affordability Crisis: How Rising Costs are Putting the Brakes on Car Sales The Extended Warranty Pitch: What Dealers Don't Always Tell You
The Extended Warranty Pitch: What Dealers Don't Always Tell You Unlock Your Dream Ride: The Ultimate Guide to Scoring a New Car Deal
Unlock Your Dream Ride: The Ultimate Guide to Scoring a New Car Deal The Ultimate Guide to Scoring a Great Deal on a Used Car
The Ultimate Guide to Scoring a Great Deal on a Used Car Used Car Paperwork Checklist: Everything You Need to Buy Smart
Used Car Paperwork Checklist: Everything You Need to Buy Smart Decoding “As-Is”: Your Essential Guide to Buying a Used Car
Decoding “As-Is”: Your Essential Guide to Buying a Used Car Allstate Auto Insurance: A Comprehensive Review
Allstate Auto Insurance: A Comprehensive Review Cars.com: Your All-in-One Guide to Buying, Selling, and Owning Cars
Cars.com: Your All-in-One Guide to Buying, Selling, and Owning Cars Carfax: Unlocking a Vehicle's History – Is It Worth It?
Carfax: Unlocking a Vehicle's History – Is It Worth It? Is Geico the Right Choice? An In-Depth Auto Insurance Review
Is Geico the Right Choice? An In-Depth Auto Insurance Review Progressive Auto Insurance: A Complete Review of Coverage, Costs, and Customer Experience
Progressive Auto Insurance: A Complete Review of Coverage, Costs, and Customer Experience The Trusted Choice: A Comprehensive Look at NAPA AutoCare Center Services
The Trusted Choice: A Comprehensive Look at NAPA AutoCare Center Services Mazda Miata: Unpacking the Thrills and the Real Cost of Ownership
Mazda Miata: Unpacking the Thrills and the Real Cost of Ownership Online Car Shopping vs. Dealerships: Which Road Should You Take?
Online Car Shopping vs. Dealerships: Which Road Should You Take? The Hidden Risks of Buy Here Pay Here Car Dealerships
The Hidden Risks of Buy Here Pay Here Car Dealerships Ford Check Engine Light On? Here's What It Means and What to Do
Ford Check Engine Light On? Here's What It Means and What to Do USAA Auto Insurance Review: The Complete In’s and Out’s (2025 Edition)
USAA Auto Insurance Review: The Complete In’s and Out’s (2025 Edition) Is an AARP Membership Worth It for Drivers?
Is an AARP Membership Worth It for Drivers? The Basics of Car Insurance Deductibles and How They Work
The Basics of Car Insurance Deductibles and How They Work Navigating Bank of America Auto Loans: What You Need to Know
Navigating Bank of America Auto Loans: What You Need to Know 5 Steps to a Higher Credit Score: Your Guide to Better Auto Loan Rates
5 Steps to a Higher Credit Score: Your Guide to Better Auto Loan Rates The General Auto Insurance: What You Need to Know
The General Auto Insurance: What You Need to Know

